Understanding Blockchain: A Simple Explanation

Blockchain technology has been making waves in various industries, from finance to healthcare. But what exactly is blockchain, and how does it work? This article aims to provide a simple and straightforward explanation of blockchain, making it accessible to everyone, regardless of their technical background.
What is Blockchain?

Blockchain is essentially a digital ledger that records transactions across many computers so that the record cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks and the consensus of the network. In simpler terms, it's a decentralized database that keeps a record of all transactions in a secure and transparent manner.
Decentralization: The Core Principle

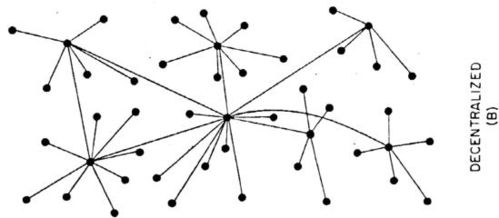
One of the key features of blockchain is its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional databases that are managed by a central authority, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network. This means that the data is distributed across multiple computers, making it nearly impossible for a single entity to control or manipulate the information.
How Does Blockchain Work?

Blockchain works through a series of interconnected blocks, each containing a list of transactions. When a new transaction occurs, it is broadcasted to the network, and nodes (computers) in the network validate the transaction. Once validated, the transaction is added to a new block and appended to the chain.
Consensus Mechanism: Ensuring Security

One of the most crucial aspects of blockchain is its consensus mechanism. This mechanism ensures that all nodes in the network agree on the validity of the transactions. There are several consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), which vary in their approach to achieving consensus.
Immutability: The Unchangeable Record

Once a block is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This is because each block contains a unique hash, which is a digital fingerprint of the block's data. If any data within the block is changed, the hash will also change, making it easy to detect tampering.
Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of the most notable applications include:
Financial Transactions: Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the financial industry by enabling secure and transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries.
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can be used to track and verify the movement of goods and services, ensuring transparency and reducing fraud.
Healthcare: Blockchain can help in securely storing and sharing patient records, improving data privacy and reducing the risk of medical errors.
Identity Verification: Blockchain can be used to create a secure and decentralized system for verifying identities, reducing the risk of identity theft.
Challenges and Limitations
While blockchain technology offers numerous benefits, it also faces some challenges and limitations:
Scalability: As the number of transactions increases, blockchain networks can become slower and more expensive to operate.
Energy Consumption: Some blockchain networks, particularly those using PoW, consume a significant amount of energy.
Regulatory Hurdles: The evolving nature of blockchain technology makes it challenging for regulators to keep up with the pace of innovation.
Conclusion

Blockchain technology is a groundbreaking innovation that has the potential to transform various industries. By understanding its core principles and applications, we can better appreciate its impact and explore its potential to create a more secure, transparent, and efficient future.
